The Global Diabetes Drugs Market is expected to reach at a CAGR of 7.8% during the forecast period 2025-2032.
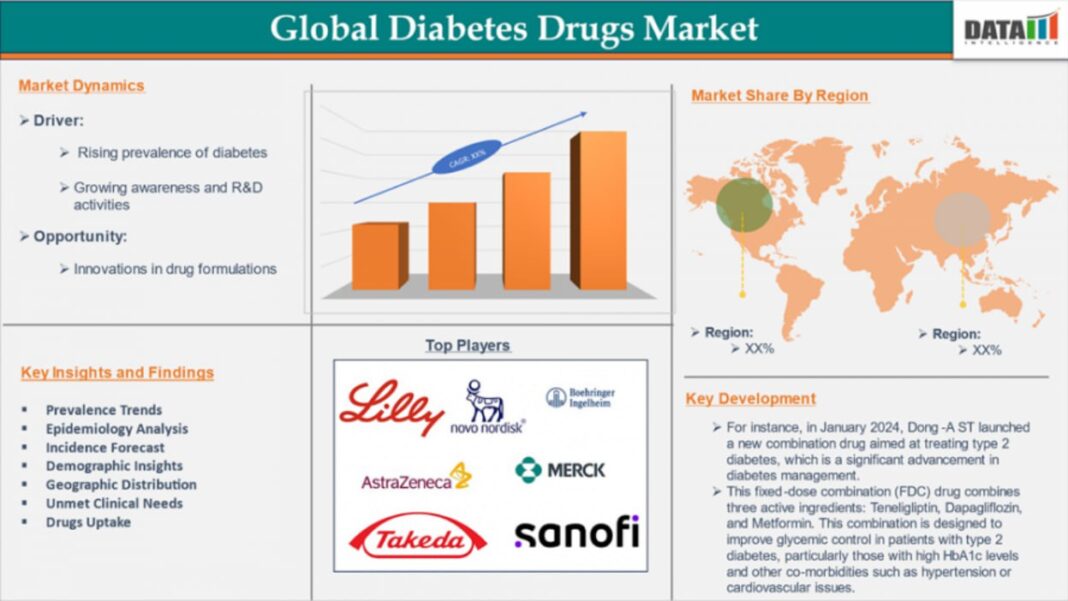
The Global Diabetes Drugs Market is experiencing strong growth due to the rising prevalence of diabetes, advancements in pharmaceutical innovation, and increasing adoption of effective treatment therapies. According to DataM Intelligence, The Global Diabetes Drugs Market was valued at US$ 78.11 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach US$ 141.73 billion by 2032, expanding at a CAGR of 7.8% during 2025–2032. The demand is largely driven by growing patient awareness, government initiatives, and improved drug accessibility across both developed and emerging economies.
A Major growth driver is the surge in Type 2 diabetes cases caused by sedentary lifestyles, obesity, and aging populations. Among drug categories, insulin and oral antidiabetic drugs dominate due to their wide prescription base and effectiveness. Geographically, North America dominates the market because of its sophisticated healthcare infrastructure, high awareness, and strong R&D presence. Asia-Pacific, however, is emerging as the fastest-growing region with increasing healthcare investments, large patient populations, and supportive government policies.
Key Highlights from the Report:
Rising prevalence of Type 2 diabetes is fueling demand for innovative drug therapies.
Insulin analogs remain the leading product category in the diabetes drugs market.
North America dominates the global market due to the availability of modern treatments.
Asia-Pacific shows fastest growth, supported by increasing healthcare expenditure.
Strategic collaborations between pharma companies are shaping market expansion.
Personalized medicine and biosimilar adoption are emerging growth opportunities.
Market Segmentation:
The Diabetes Drugs Market can be segmented based on drug class, route of administration, and end-user applications. By drug class, the market includes insulin analogs, oral antidiabetics (sulfonylureas, biguanides, DPP-4 inhibitors, SGLT2 inhibitors, and GLP-1 receptor agonists), and combination therapies. Among these, oral antidiabetics currently hold a significant share due to their ease of use and broad adoption, while SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists are gaining traction because of their cardiovascular benefits.
By route of administration, the market is divided into oral and injectable formulations. Oral drugs dominate due to patient compliance and convenience, while injectables, particularly insulin analogs, remain critical for Type 1 diabetes management.
In terms of end-users, the market is segmented into hospitals, specialty clinics, and retail pharmacies. Retail pharmacies contribute significantly as they provide accessible medication to large patient populations, whereas hospitals and specialty clinics play a vital role in advanced treatment delivery.